- You are here:
- Home »
- Blog »
- CMA Exam Details »
- CMA Entrance Exam Curriculum by Parts and Topics
CMA Entrance Exam Curriculum by Parts and Topics
In order to become a CMA in the US, you have to go through the CMA entrance exam. What exactly does it cover? Is it very difficult? Let’s take a look.
CMA Entrance Exam: The Format
The exam is 100% computerized with 100 multiple choice questions and two 30-minute essay questions. It consists of the following parts:
- Financial Planning, Performance and Control
- Financial Decision Making
Candidates are free to take either one or both parts of the exam within the same test windows. The exams have to be completed within 3 years, counting from the date the candidates pay the entrance fee.
New CMA Exam Format Effective 2015
This page is now updated with the latest syllabus. The 3 major changes are:
- Additional content related to external financial reporting in Part 1
- A new section on strategic planning included in Planning, budgeting and forecasting in Part 1
- Professional ethics now tested only in Part 2
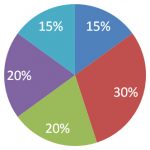
CMA Exam Part 1
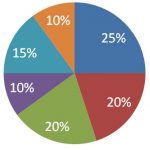
CMA Exam Part 2
- Financial statement analysis (25%)
- Corporate finance (20%)
- Decision analysis (20%)
- Risk management (10%)
- Investment decisions (15%)
- Professional ethics (10%)
More Information On Each Topic
CMA Exam Part 1
External Financial Reporting Decision
- New to the CMA exam covering basis of financial accounting.
- Preparation of financial statements.
- Valuation of assets and liabilities.
- Operating and capital leases.
- Impact of equity transactions.
- Revenue recognition; income measurement; major differences between U.S. GAAP and IFRS.
Planning, budgeting, and forecasting
- How to annual profit plans and supporting schedules.
- Different types of budget e.g. activity-based budgeting, project budgeting and flexible budgeting.
- Top-level planning and analysis.
- Forecasting including quantitative methods e.g. regression analysis and learning curves.
Performance Management
- How to analyze the finance statement items such as revenue, cost, profit and investment in assets.
- Variance analysis based on flexible budgets and standard costs.
- Responsibility accounting for revenue, cost, contribution and profit centers.
- Balanced scorecards
Cost Management
- Cost concepts, flows and terminology.
- Alternative cost objectives.
- Cost measurement concepts.
- Cost accumulation system e.g. job order costing, process costing, activity-based costing.
- Overhead cost allocation.
- Operational efficiency and business process performance topics e.g. JIT, MRP, theory of constraints, value chain analysis, benchmarking, ABM and continuous improvement.
Internal Control
- Risk assessment
- Internal control environment, procedures and standards.
- Responsibility and authority of internal auditing.
- Types of audits.
- Assessing the adequacy of accounting information systems control.
CMA Exam Part 2
Financial Statement Analysis
- Principal financial statements and their uses.
- Limitation of financial statement information.
- Interpretation and analysis of financial statement e.g. ratio and comparative analyses.
- Market value vs book value.
- Fair value accounting.
- Major difference between IFRS and US GAAP.
- Off-balance sheet financing.
- Cash-flow statement preparation, analysis and reconciliation.
- Earnings quality.
Corporate Finance
- Types of risk.
- Measures of risk.
- Portfolio management.
- Options and futures.
- Capital instruments for long-term financing.
- Dividend policy.
- Factors influencing the optimal capital structure.
- Cost of capital.
- Managing and financing working capital.
- Mergers and acquisitions.
- International finance.
Decision Analysis
- Relevant data concepts.
- Cost-volume-profit analysis.
- Marginal analysis.
- Make vs buy decisions.
- Pricing.
- Income tax implications for operational decision analysis.
- ERM.
Risk Management
- Operational risk, Hazard risk and financial risk and strategic risk.
Investment Decision
- Cash flow estimates.
- Concepts of DCF (discounted cash flow), net present value, IRR (internal rate of return).
- Non-discounting analysis techniques.
- Income tax implications for investment decisions.
- Ranking investment projects.
- Risk analysis.
- Real options.
- Valuation models.
Professional Ethics
- Ethical consideration for both management accountants and the organization.
Next Reading: The Exam’s Format
Structure and Duration
For Your Further Reading
Exam content, pass rate trend and difficulty of:
For specific information on the CMA entrance exam together with study tips and exam tactics, please consider signing up for our free mini course here:
Join us if you want to get tips on how to plan,
study and pass your CMA exam… on your first attempt!
Source: CMA Candidate Handbook
About the Author Stephanie Ng
I am the author of How to Pass The CPA Exam (published by Wiley) and the publisher of this and several accounting professional exam prep sites.