- You are here:
- Home »
- Blog »
- CMA Exam Details »
- CMA Entrance Exam Curriculum by Parts and Topics
CMA Entrance Exam Curriculum by Parts and Topics
In order to become a CMA in the US, you have to go through the CMA entrance exam. What exactly does it cover? Is it very difficult? Let’s take a look.
CMA Entrance Exam: The Format
The exam is 100% computerized with 100 multiple choice questions and two 30-minute essay questions. It consists of the following parts:
- Financial Planning, Performance and Control
- Financial Decision Making
Candidates are free to take either one or both parts of the exam within the same test windows. The exams have to be completed within 3 years, counting from the date the candidates pay the entrance fee.
New CMA Exam Format Effective 2015
This page is now updated with the latest syllabus. The 3 major changes are:
- Additional content related to external financial reporting in Part 1
- A new section on strategic planning included in Planning, budgeting and forecasting in Part 1
- Professional ethics now tested only in Part 2
Candidates who took the exam before 2015 and would like more details on the changes, please check out the summary on IMA website or detailed version on this site.
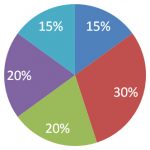
CMA Exam Part 1
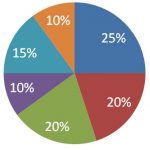
CMA Exam Part 2
- Financial statement analysis (25%)
- Corporate finance (20%)
- Decision analysis (20%)
- Risk management (10%)
- Investment decisions (15%)
- Professional ethics (10%)
More Information On Each Topic
CMA Exam Part 1
External Financial Reporting Decision
- New to the CMA exam covering basis of financial accounting.
- Preparation of financial statements.
- Valuation of assets and liabilities.
- Operating and capital leases.
- Impact of equity transactions.
- Revenue recognition; income measurement; major differences between U.S. GAAP and IFRS.
Planning, budgeting, and forecasting
- How to annual profit plans and supporting schedules.
- Different types of budget e.g. activity-based budgeting, project budgeting and flexible budgeting.
- Top-level planning and analysis.
- Forecasting including quantitative methods e.g. regression analysis and learning curves.
Performance Management
- How to analyze the finance statement items such as revenue, cost, profit and investment in assets.
- Variance analysis based on flexible budgets and standard costs.
- Responsibility accounting for revenue, cost, contribution and profit centers.
- Balanced scorecards
Cost Management
- Cost concepts, flows and terminology.
- Alternative cost objectives.
- Cost measurement concepts.
- Cost accumulation system e.g. job order costing, process costing, activity-based costing.
- Overhead cost allocation.
- Operational efficiency and business process performance topics e.g. JIT, MRP, theory of constraints, value chain analysis, benchmarking, ABM and continuous improvement.
Internal Control
- Risk assessment
- Internal control environment, procedures and standards.
- Responsibility and authority of internal auditing.
- Types of audits.
- Assessing the adequacy of accounting information systems control.
CMA Exam Part 2
Financial Statement Analysis
- Principal financial statements and their uses.
- Limitation of financial statement information.
- Interpretation and analysis of financial statement e.g. ratio and comparative analyses.
- Market value vs book value.
- Fair value accounting.
- Major difference between IFRS and US GAAP.
- Off-balance sheet financing.
- Cash-flow statement preparation, analysis and reconciliation.
- Earnings quality.
Corporate Finance
- Types of risk.
- Measures of risk.
- Portfolio management.
- Options and futures.
- Capital instruments for long-term financing.
- Dividend policy.
- Factors influencing the optimal capital structure.
- Cost of capital.
- Managing and financing working capital.
- Mergers and acquisitions.
- International finance.
Decision Analysis
- Relevant data concepts.
- Cost-volume-profit analysis.
- Marginal analysis.
- Make vs buy decisions.
- Pricing.
- Income tax implications for operational decision analysis.
- ERM.
Risk Management
- Operational risk, Hazard risk and financial risk and strategic risk.
Investment Decision
- Cash flow estimates.
- Concepts of DCF (discounted cash flow), net present value, IRR (internal rate of return).
- Non-discounting analysis techniques.
- Income tax implications for investment decisions.
- Ranking investment projects.
- Risk analysis.
- Real options.
- Valuation models.
Professional Ethics
- Ethical consideration for both management accountants and the organization.
Next Reading: The Exam’s Format
Structure and Duration
For Your Further Reading
Exam content, pass rate trend and difficulty of:
For specific information on the CMA entrance exam together with study tips and exam tactics, please consider signing up for our free mini course here:
Join us if you want to get tips on how to plan,
study and pass your CMA exam… on your first attempt!
Source: CMA Candidate Handbook
About the Author Stephanie Ng
I am the author of How to Pass The CPA Exam (published by Wiley) and the publisher of this and several accounting professional exam prep sites.